Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic Awareness For Kindergarten
Sequencing Phonemic Awareness Skills
Phonemic awareness instruction typically spans two years, kindergarten and first grade. Oral activities in kindergarten focus on simple tasks such as rhyming, matching words with beginning sounds, and blending sounds into words. In first grade, phonemic awareness tasks are more advanced, focusing on blending ('Blend these sounds together 'mmmm-aaaa-nnnn), segmentation ('What are the sounds in man?), and the substitution and manipulation of phonemes (e.g., Change the first sound in man to /r/. What word do you have?').
Phonemic Awareness Development Continuum
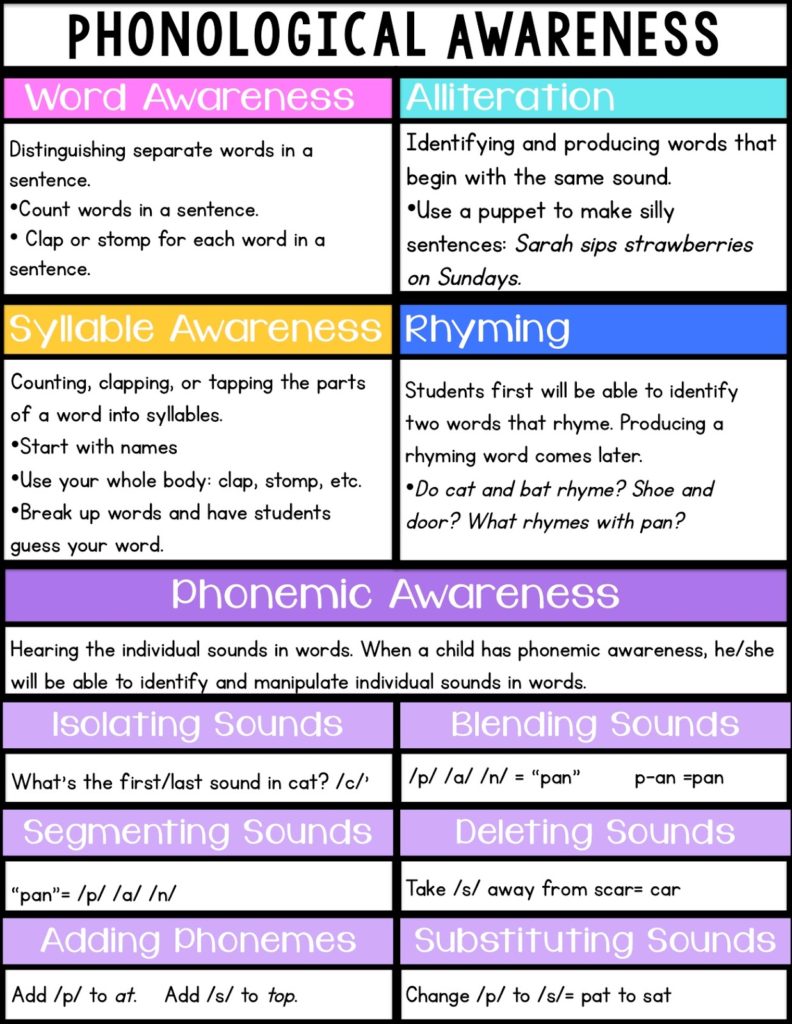
Phonemic awareness is the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate individual sounds-phonemes-in spoken words. Before children learn to read print, they need to become more aware of how the sounds in words work.
- Phonemic awareness refers to the specific ability to focus on and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken words. Phonemes are the smallest units comprising spoken language. Phonemes combine to form syllables and words. For example, the word 'mat' has three phonemes: /m/ /a/ /t/.
- Phonemic awareness is the ability to hear, identify, and manipulate individual sounds-phonemes-in spoken words. Before children learn to read print, they need to become more aware of how the sounds in words work. They must understand that words are made up of speech sounds, or phonemes (the smallest parts of sound in a spoken word that make a.
- Phonemic awareness is the ability to notice, think about, and work with the individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken words. Manipulating the sounds in words includes blending, stretching, or otherwise changing words. Children can demonstrate phonemic awareness in several ways, including.
- Phonemic awareness is an essential skill that underlies a child's ability to learn to read and spell. Phonemic awareness falls under the umbrella of phonological awareness; however, it only pertains to the phonemes (sounds) in words.
Examples of Phonemic Awareness Skills
- Sound and Word discrimination: What word doesn't belong with the others: 'cat', 'mat', 'bat', 'ran'? 'ran'
- Rhyming: What word rhymes with 'cat'? bat
- Syllable splitting: The onset of 'cat' is /k/, the rime is /at/
- Blending: What word is made up of the sounds /k/ /a/ /t/? 'cat'
- Phonemic segmentation: What are the sounds in 'cat'? /k/ /a/ /t/
- Phoneme deletion: What is 'cat' without the /k/? 'at'
- Phoneme manipulation: What word would you have if you changed the /t/ in cat to an /n/? 'can'
Curriculum Maps
Michael Heggerty Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic awareness skills can be taught in a particular sequence that maximizes student understanding and instructional efficiency. Phonemic awareness is only taught in kindergarten and first grade. By the end of first grade, students should have a firm grasp of phonemic awareness.

Phonemic Awareness Activities

Curriculum maps list specific skills that relate to each big idea. Each skill can be taught during at an optimal time during the school year.
Click here for an explanation of how to read curriculum maps.
TIP: Go to the Curriculum Maps page in the Resources section to view and download Curriculum Maps for each Big Idea and grade.
How to read curriculum maps
The numbers in the top row of the curriculum map correspond to the months of the school year. For example, if your school year begins in September, then September would be month 1 on the map. If your school year begins in August, then August would be month one.
The shaded boxes marked with 'X' represent the months in which a particular skill should be taught.
The map can be read using either a 'horizontal trace' or a 'vertical trace'. To do a horizontal trace, you select a skill you are interested in, then trace across the row to find the months marked with an 'X' for that skill. This will tell you which months a skill should be taught. To perform a vertical trace, select a particular month, then trace down the column to find the shaded boxes. The shaded boxes correspond to the skills that should be taught that month.